(Created page with "=== Exfoliants === Exfoliants are products designed to remove dead cells from the surface of the skin. They are important for promoting healthy skin and increasing the efficacy of other skincare products, but they require careful and periodic use. While both AHAs and BHAs act as skin exfoliants, AHAs are what is known as “water-soluble,” and BHAs are considered “oil soluble.” What this means is that AHAs work on the skin's surface, while BHAs (like salicylic aci...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Skin Care]] | |||
== Exfoliation == | |||
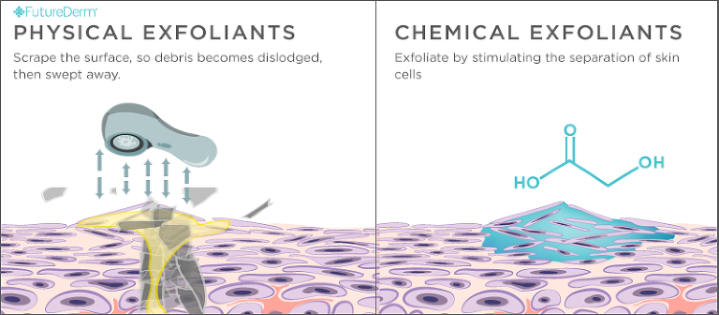
'''<u><big>Exfoliation</big></u>''' is the process of encouraging the renewal of skin cells by removing dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. This is achieved by either '''chemical (topical products)''' or '''physical (topical products and cosmetic tools)''' means. '''Exfoliating''' is important for promoting healthy skin and increasing the efficacy of other skincare products, but they require ''careful'' and ''periodic'' use. There are many signs that skin can benefit from exfoliation, such as clogged pores, dullness, texture, roughness, uneven tone and frequent breakouts. | |||
=== Serums == | * '''Chemical''' '''Exfoliation''' is one of the two main categories that exfoliating products fall into. Most chemical exfoliants work by breaking down the glue or bonds between dead skin cells and promoting its shedding. | ||
Serums are | ** '''Chemical exfoliants''' can be further categorized into '''AHAs (alpha hydroxy acids)''', '''PHAs (poly hydroxy acids),''' which are water-soluble chemicals, and '''BHAs (beta hydroxy acids)''', which are lipid-soluble chemicals. | ||
** Common '''chemical exfoliants''' found in products are '''salicylic acid (BHA), glycolic acid, lactic acid (AHAs)''' and '''gluconolactone (PHAs).''' | |||
* The other category can be referred to as '''physical (aka mechanical) exfoliation,''' which involves products and skin tools. Most products in this category are referred to as scrubs or polishes, that contain granules which physically buff or exfoliate away dead skin cells. Skin tools are sometimes used instead of products, | |||
[[File:Exfoliants.png|thumb|719x719px|https://www.majormag.in/physical-vs-chemical-exfoliation-peels-and-scrubs/]] | |||
=== Choosing Exfoliants === | |||
Choosing the right exfoliant product depends on skin concerns, most skin types will benefit from chemical leave on treatments, such as toners, serums and moisturizers that contain exfoliants. Sensitive and irritated skin types will benefit from wash off treatments, such as cleansers or masks that contain exfoliants. Mature, healthy and tough skin will benefit from physical exfoliants and scrubs. It is usually recommended to use chemical exfoliants on the face and body (entire body), and preferably physical exfoliants solely on the body (neck below). | |||
=== Using Exfoliants === | |||
When using a leave on treatment product containing an exfoliant, it is recommended to use 1-3x a week, preferably at night, without layering or mixing other exfoliating products. | |||
When using a wash off treatment product containing an exfoliant, it is recommended to leave the product on the skin for 1-5 minutes before rinsing off, to ensure penetration of the ingredients. Due to the differing solubility and mechanisms between chemical exfoliants, products containing them should be chosen for specific skin concerns. It is often recommended that oily, combination and acne prone skin types should lean towards '''BHA''' usage and dry and normal skin types should lean towards '''AHA''' usage. If skin is sensitive or compromised, '''PHAs, mandelic acid''' or '''enzymes''' should be used instead. | |||
== Serums == | |||
[[File:Serum2.png|thumb|Common serum appearance]] | |||
<big>'''<u>Serums</u>'''</big> are defined as concentrated topical products, which can come under many names, ('''essences''', which are typically hydrating and '''ampoules''') that can have a wide variety of uses, for example '''hydrating''' or '''brightening'''. They usually contain higher percentages of active or desired ingredients for treating a skin concern. Water and lipid contents are two core parts of the skins physiology and structure, maintaining '''balance''' with '''hydration''' and '''moisturizing''' can be extremely important for promoting radiant, healthy and even skin. | |||
=== Choosing Serum(s) === | |||
Choosing the right '''serum''' depends on skin concerns. All skin types will benefit from '''serums''' that contain '''hydrating''' and '''moisturizing''' ingredients to help support the skins natural barrier, usually due to ingredients such as '''hyaluronic acid (and its related derivatives such as sodium hyaluronate), glycerin, urea or beta-glucan.''' | |||
* When pigmentation and uneven tone are of concern you should look for '''brightening serums''' that contain ingredients such as '''tranexamic acid, retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin etc, azelaic acid or niacinamide (Vitamin B3).''' | |||
* When acne and blemishes are of concern you should look for any serum that contains '''retinoids, azelaic acid, niacinamide, benzoyl peroxide or exfoliants''' in your serums. | |||
* When aging of the skin is of concern, ingredients like '''retinoids, vitamin C''' and '''antioxidants''' in general can be very beneficial. | |||
* If skin is sensitive, irritated or compromised you should look for serums that contain '''Panthenol (Vitamin B5), allantoin, centella asiatica (aka cica, and derivatives like madecassoside)''' and '''aloe vera.''' | |||
=== Using Serums === | |||
It is important to incorporate '''hydrating, soothing''' and '''moisturizing''' '''serums''' into your routine. It is often recommended to only use '''1-2''' sometimes '''3''' '''serums''' (whether they be labelled as essences or ampoules) at a time. You should try to avoid combining concern treating ingredients (which are referred to as '''actives)''' at once, unless multiple are included in the serum or they are known to work well together (It is also recommended to only use '''1-4 active''' ingredients in your routine at all, excluding '''hydrating''' and '''moisturizing actives'''). | |||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 8 December 2023
Exfoliation
Exfoliation is the process of encouraging the renewal of skin cells by removing dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. This is achieved by either chemical (topical products) or physical (topical products and cosmetic tools) means. Exfoliating is important for promoting healthy skin and increasing the efficacy of other skincare products, but they require careful and periodic use. There are many signs that skin can benefit from exfoliation, such as clogged pores, dullness, texture, roughness, uneven tone and frequent breakouts.
- Chemical Exfoliation is one of the two main categories that exfoliating products fall into. Most chemical exfoliants work by breaking down the glue or bonds between dead skin cells and promoting its shedding.
- Chemical exfoliants can be further categorized into AHAs (alpha hydroxy acids), PHAs (poly hydroxy acids), which are water-soluble chemicals, and BHAs (beta hydroxy acids), which are lipid-soluble chemicals.
- Common chemical exfoliants found in products are salicylic acid (BHA), glycolic acid, lactic acid (AHAs) and gluconolactone (PHAs).
- The other category can be referred to as physical (aka mechanical) exfoliation, which involves products and skin tools. Most products in this category are referred to as scrubs or polishes, that contain granules which physically buff or exfoliate away dead skin cells. Skin tools are sometimes used instead of products,
Choosing Exfoliants
Choosing the right exfoliant product depends on skin concerns, most skin types will benefit from chemical leave on treatments, such as toners, serums and moisturizers that contain exfoliants. Sensitive and irritated skin types will benefit from wash off treatments, such as cleansers or masks that contain exfoliants. Mature, healthy and tough skin will benefit from physical exfoliants and scrubs. It is usually recommended to use chemical exfoliants on the face and body (entire body), and preferably physical exfoliants solely on the body (neck below).
Using Exfoliants
When using a leave on treatment product containing an exfoliant, it is recommended to use 1-3x a week, preferably at night, without layering or mixing other exfoliating products.
When using a wash off treatment product containing an exfoliant, it is recommended to leave the product on the skin for 1-5 minutes before rinsing off, to ensure penetration of the ingredients. Due to the differing solubility and mechanisms between chemical exfoliants, products containing them should be chosen for specific skin concerns. It is often recommended that oily, combination and acne prone skin types should lean towards BHA usage and dry and normal skin types should lean towards AHA usage. If skin is sensitive or compromised, PHAs, mandelic acid or enzymes should be used instead.
Serums

Serums are defined as concentrated topical products, which can come under many names, (essences, which are typically hydrating and ampoules) that can have a wide variety of uses, for example hydrating or brightening. They usually contain higher percentages of active or desired ingredients for treating a skin concern. Water and lipid contents are two core parts of the skins physiology and structure, maintaining balance with hydration and moisturizing can be extremely important for promoting radiant, healthy and even skin.
Choosing Serum(s)
Choosing the right serum depends on skin concerns. All skin types will benefit from serums that contain hydrating and moisturizing ingredients to help support the skins natural barrier, usually due to ingredients such as hyaluronic acid (and its related derivatives such as sodium hyaluronate), glycerin, urea or beta-glucan.
- When pigmentation and uneven tone are of concern you should look for brightening serums that contain ingredients such as tranexamic acid, retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin etc, azelaic acid or niacinamide (Vitamin B3).
- When acne and blemishes are of concern you should look for any serum that contains retinoids, azelaic acid, niacinamide, benzoyl peroxide or exfoliants in your serums.
- When aging of the skin is of concern, ingredients like retinoids, vitamin C and antioxidants in general can be very beneficial.
- If skin is sensitive, irritated or compromised you should look for serums that contain Panthenol (Vitamin B5), allantoin, centella asiatica (aka cica, and derivatives like madecassoside) and aloe vera.
Using Serums
It is important to incorporate hydrating, soothing and moisturizing serums into your routine. It is often recommended to only use 1-2 sometimes 3 serums (whether they be labelled as essences or ampoules) at a time. You should try to avoid combining concern treating ingredients (which are referred to as actives) at once, unless multiple are included in the serum or they are known to work well together (It is also recommended to only use 1-4 active ingredients in your routine at all, excluding hydrating and moisturizing actives).