(created lipo page) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
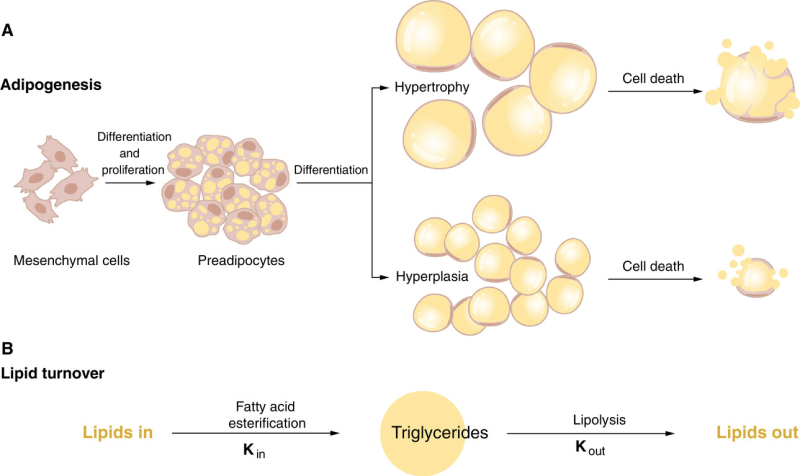
Lipolysis is the process by which fat cells (adipose tissue) reduce in size or get eliminated to free up the energy stored in them. The energy is stored as triglycerides which then get converted to fatty acids and glycerol that your body can use directly for muscles and other organs. | Lipolysis is the process by which fat cells (adipose tissue) reduce in size or get eliminated to free up the energy stored in them. The energy is stored as triglycerides which then get converted to fatty acids and glycerol that your body can use directly for muscles and other organs. Visceral fat is internal and surrounds organs and subcutaneous fat sits closer to the surface between the layers of muscle and skin. | ||
[[File:Fat cell turnover.png|800x800px]] | [[File:Fat cell turnover.png|800x800px]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The only way to remove fat in a specific area is with special medical procedures developed to target fat. | The only way to remove fat in a specific area is with special medical procedures developed to target fat. | ||
==== Injection Lipolysis ==== | |||
This is a relatively cheap and quick option often used for smaller areas, a syringe is used to inject a liquid in the fat layer under skin which disrupts fat cells and allows them to be metabolized by the body. Phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid are the most commonly used solutions for injection lipolysis.<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6128158/</ref> Aqualyx uses phosphatidylcholine and Kybella uses deoxycholic acid. Can potentially be DIYed. | |||
Liposuction | ==== Liposuction ==== | ||
Common yet relatively expensive procedure in which a large amount of fat is suctioned out of the body through a cannula (a hollow tube). It requires general, regional or local anesthesia and takes 1-3 hours to complete at a clinic.<ref>https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33252626/</ref> | |||
Laser Lipo | ==== Laser Lipo ==== | ||
A specific frequency of radiofrequency waves are emitted from a device targeted to fat cells which disrupts their membranes and causes triglycerides to be released and fat cells to gradually get eliminated<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3140909/</ref>. This method was originally used as a way to improve the effectiveness of liposuction by applying it through a tube inside the body.<ref>https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/issues/articles/vol27_i4_Laser-Assisted_Liposuction.pdf</ref> Newer methods involve using pads which can be applied to the surface of the skin and still target subcutaneous fat. | |||
'''Low Level Laser Therapy''' is a subset of laser lipo which uses RF waves with length <650nm. This applies heat and can cause eventual cell death. However certain studies show that this form of lipo causes fat cells to slowly "leak" over time which affects metabolism and may induce overall fat reduction, thus not suitable for the strict goal of targeted fat removal.<ref>https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10103-016-2021-9</ref><ref>https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/lsm.22007</ref><ref>https://erchonia.com.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/BODY-CONTOURING-USING-635NM-LOW-LEVEL-LASER-THERAPY01-nestor_body-contouring-using-635nm-laser_cutaneous-medicine-and-surgery-journal_2013.pdf</ref> | |||
Ultrasonic Cavitation | ==== Coolsculpting ==== | ||
This method involves using cold temperatures applied to the surface of the body above fat deposits, causing fat cells to freeze and die without damaging the skin. | |||
==== Ultrasonic Cavitation ==== | |||
A device emits high frequency sound vibrations which are able to disrupt fat cells under skin, effectively making them burst and get metabolized by the body. | |||
All of the above methods show moderate effectiveness for targeted fat removal and the application varies between professional clinic services and at-home devices which work at different power levels. For a comparison of methods see these studies: | |||
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20123238437 | |||
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/lsm.22475 | |||
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.15929 | |||
https://it.fillmed.com/uploads/generic_file/bio-skin-gineering._a_novel_method_to_aging_treatment..pdf | |||
Revision as of 03:49, 3 April 2024
Lipolysis is the process by which fat cells (adipose tissue) reduce in size or get eliminated to free up the energy stored in them. The energy is stored as triglycerides which then get converted to fatty acids and glycerol that your body can use directly for muscles and other organs. Visceral fat is internal and surrounds organs and subcutaneous fat sits closer to the surface between the layers of muscle and skin.
It's important to note that normal weight loss does not get rid of fat cells but only shrinks their size. Fat cells will naturally be removed during their lifecycle (cell turnover) at a rate of 10% per year.[1]
Weight loss will also eliminate fat from all areas of the body at once, although hormonal factors will influence how much is maintained in a gynoid or android fat pattern. This means you can not remove fat in a specific area using exercise which makes it harder to shape your body.
The only way to remove fat in a specific area is with special medical procedures developed to target fat.
Injection Lipolysis
This is a relatively cheap and quick option often used for smaller areas, a syringe is used to inject a liquid in the fat layer under skin which disrupts fat cells and allows them to be metabolized by the body. Phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid are the most commonly used solutions for injection lipolysis.[2] Aqualyx uses phosphatidylcholine and Kybella uses deoxycholic acid. Can potentially be DIYed.
Liposuction
Common yet relatively expensive procedure in which a large amount of fat is suctioned out of the body through a cannula (a hollow tube). It requires general, regional or local anesthesia and takes 1-3 hours to complete at a clinic.[3]
Laser Lipo
A specific frequency of radiofrequency waves are emitted from a device targeted to fat cells which disrupts their membranes and causes triglycerides to be released and fat cells to gradually get eliminated[4]. This method was originally used as a way to improve the effectiveness of liposuction by applying it through a tube inside the body.[5] Newer methods involve using pads which can be applied to the surface of the skin and still target subcutaneous fat.
Low Level Laser Therapy is a subset of laser lipo which uses RF waves with length <650nm. This applies heat and can cause eventual cell death. However certain studies show that this form of lipo causes fat cells to slowly "leak" over time which affects metabolism and may induce overall fat reduction, thus not suitable for the strict goal of targeted fat removal.[6][7][8]
Coolsculpting
This method involves using cold temperatures applied to the surface of the body above fat deposits, causing fat cells to freeze and die without damaging the skin.
Ultrasonic Cavitation
A device emits high frequency sound vibrations which are able to disrupt fat cells under skin, effectively making them burst and get metabolized by the body.
All of the above methods show moderate effectiveness for targeted fat removal and the application varies between professional clinic services and at-home devices which work at different power levels. For a comparison of methods see these studies:
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20123238437
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/lsm.22475
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.15929
- ↑ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/joim.13435
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6128158/
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33252626/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3140909/
- ↑ https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/issues/articles/vol27_i4_Laser-Assisted_Liposuction.pdf
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10103-016-2021-9
- ↑ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/lsm.22007
- ↑ https://erchonia.com.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/BODY-CONTOURING-USING-635NM-LOW-LEVEL-LASER-THERAPY01-nestor_body-contouring-using-635nm-laser_cutaneous-medicine-and-surgery-journal_2013.pdf