Unusualcrow (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=== Anatomy of Hair<ref>{{Cite web |title=Hair Follicle |url=https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23435-hair-follicle |access-date=Nov 6, 2023 |website=Cleveland Clinic}}</ref> === | === Anatomy of Hair<ref>{{Cite web |title=Hair Follicle |url=https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23435-hair-follicle |access-date=Nov 6, 2023 |website=Cleveland Clinic}}</ref> === | ||
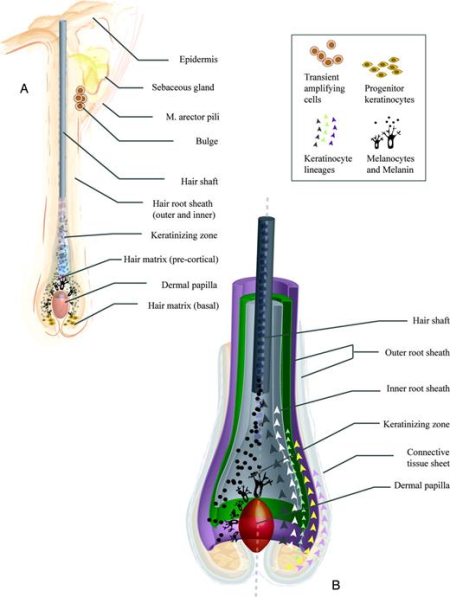
Hair follicles are located within the first two layers of your skin—the epidermis and the dermis. An individual hair follicle consists of a few different parts; it is primarily the '''root''' (dermal papilla), the '''shaft''' (or strand), and the '''sebaceous gland''' that we are concerned with. | Hair follicles are located within the first two layers of your skin—the epidermis and the dermis. An individual hair follicle consists of a few different parts; it is primarily the '''root''' (dermal papilla), the '''shaft''' (or strand), and the '''sebaceous gland''' that we are concerned with. | ||
[[File:Hair Structure.png|thumb|500x500px|The strand is a highly organised structure and is made up of three main parts. Starting at the hair surface and working in, there is the cuticle, followed by the cortex and then the medulla in the centre. The medulla is not found within every hair fibre, with thicker fibres being more lightly to possess medulla.<ref>https://www.hairknowhow.com/know-your-hair-structure</ref>]] | |||
[[File:Hair_follicle_anatomy.png|597x597px]] | |||
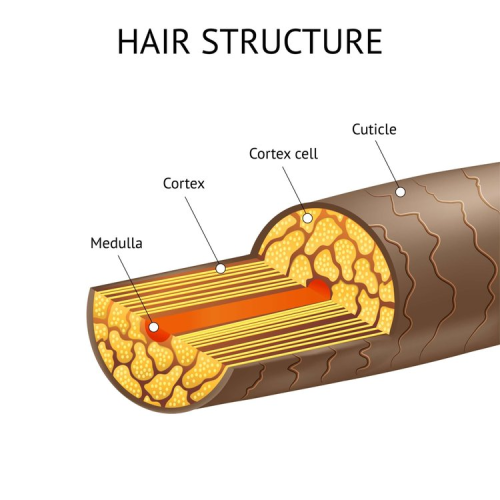
==== Cuticle ==== | |||
The cuticle comprises 8-10 layers of flat overlapping translucent cells - meaning they are essentially transparent, like window glass. The primary role of the cuticle is to protect the underlying cortex. | |||
The health of the cuticle is vital because it affects the hydration, texture, feel and glossiness/shine of your hair. The surface of the cuticle is hydrophobic (water-hating), which means that the cuticle readily binds to oils and other hydrophobic substances. Hair sprays, mousses and gels all act directly on the cuticle. The cuticle is physically damaged by brushing, especially when wet. Commercial hair care products containing active chemicals, e.g. peroxide or thioglycolate (dyeing and perming solution, respectively), disrupt and lift the cuticle, increasing cuticle loss. Products such as conditioners and oils soften the cuticle making it less brittle, reducing loss. | |||
==== Cortex ==== | |||
The cortex is in the centre of each hair fibre and consists of long, tightly packed keratin spindles stabilised by disulphide bonds. The cortex gives hair its strength and is also home to melanin granules. These are packets of pigment that are responsible for your hair colour. The cortex is also responsible for giving hair its shape and texture, resulting in your hair being either straight, wavy, curly or kinky. | |||
Everyday hair care products that can damage the cortex include perming, curling, straightening and bleaching solutions. The chemicals within these products penetrate your hair and destabilise the disulphide bonds within the cortex, both weakening and disorganising it. Chemical treatments ultimately increase the porosity of hair (creating holes and cracks within the cortex), resulting in hair fibres increasing from low porosity to high porosity hair. | |||
==== Medulla ==== | |||
The medulla is located at the centre of many but not all hair fibres - typically within thicker, coarser terminal hair. If present, the medulla may also be discontinuous, meaning that it is patchy and does not run through the entire hair fibre length. The medulla has a higher lipid content and has reduced disulfide bonds in comparison to other hair structures | |||
=== Hair Growth === | |||
* '''Anagen:''' begins at the root, where the hair gets its blood supply and nutrients it needs to grow, taking anywhere between 2 to 7 years in this stage. | |||
* '''Catagen:''' transitioning the hair from a phase of growth to a phase of rest for approximately two weeks. In this stage, the hair detaches from the blood supply at the root. | |||
* T'''elogen:''' the hair sheds, detaching the shaft from the follicle within a period of 4 months. | |||
=== Dihydrotestosterone and Male Pattern Hair Loss === | === Dihydrotestosterone and Male Pattern Hair Loss === | ||
Male pattern hair loss is primarily caused by genetics and dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. High levels of DHT can shrink the hair follicles and cause hair loss.<ref>Cleveland Clinic. ('''12/20/2022'''). DHT (Dihydrotestosterone). ''Cleveland Clinic.'' <nowiki>https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24555-dht-dihydrotestosterone</nowiki></ref> A DHT blocker such as dutasteride, finasteride can be used to prevent further hair loss, and minoxidil can be an effective treatment for hair loss. However, if you have testosterone suppressed, you likely don't need to block DHT. | <references />Male pattern hair loss is primarily caused by genetics and dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. High levels of DHT can shrink the hair follicles and cause hair loss.<ref>Cleveland Clinic. ('''12/20/2022'''). DHT (Dihydrotestosterone). ''Cleveland Clinic.'' <nowiki>https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24555-dht-dihydrotestosterone</nowiki></ref> A DHT blocker such as dutasteride, finasteride can be used to prevent further hair loss, and minoxidil can be an effective treatment for hair loss. However, if you have testosterone suppressed, you likely don't need to block DHT. | ||
Revision as of 06:45, 19 January 2024
Taking good care of your hair is an important component of cosmetology. It is one of the first things that everyone sees, and good hair can greatly improve someone's general appearance.
Anatomy of Hair[1]
Hair follicles are located within the first two layers of your skin—the epidermis and the dermis. An individual hair follicle consists of a few different parts; it is primarily the root (dermal papilla), the shaft (or strand), and the sebaceous gland that we are concerned with.
Cuticle
The cuticle comprises 8-10 layers of flat overlapping translucent cells - meaning they are essentially transparent, like window glass. The primary role of the cuticle is to protect the underlying cortex.
The health of the cuticle is vital because it affects the hydration, texture, feel and glossiness/shine of your hair. The surface of the cuticle is hydrophobic (water-hating), which means that the cuticle readily binds to oils and other hydrophobic substances. Hair sprays, mousses and gels all act directly on the cuticle. The cuticle is physically damaged by brushing, especially when wet. Commercial hair care products containing active chemicals, e.g. peroxide or thioglycolate (dyeing and perming solution, respectively), disrupt and lift the cuticle, increasing cuticle loss. Products such as conditioners and oils soften the cuticle making it less brittle, reducing loss.
Cortex
The cortex is in the centre of each hair fibre and consists of long, tightly packed keratin spindles stabilised by disulphide bonds. The cortex gives hair its strength and is also home to melanin granules. These are packets of pigment that are responsible for your hair colour. The cortex is also responsible for giving hair its shape and texture, resulting in your hair being either straight, wavy, curly or kinky.
Everyday hair care products that can damage the cortex include perming, curling, straightening and bleaching solutions. The chemicals within these products penetrate your hair and destabilise the disulphide bonds within the cortex, both weakening and disorganising it. Chemical treatments ultimately increase the porosity of hair (creating holes and cracks within the cortex), resulting in hair fibres increasing from low porosity to high porosity hair.
Medulla
The medulla is located at the centre of many but not all hair fibres - typically within thicker, coarser terminal hair. If present, the medulla may also be discontinuous, meaning that it is patchy and does not run through the entire hair fibre length. The medulla has a higher lipid content and has reduced disulfide bonds in comparison to other hair structures
Hair Growth
- Anagen: begins at the root, where the hair gets its blood supply and nutrients it needs to grow, taking anywhere between 2 to 7 years in this stage.
- Catagen: transitioning the hair from a phase of growth to a phase of rest for approximately two weeks. In this stage, the hair detaches from the blood supply at the root.
- Telogen: the hair sheds, detaching the shaft from the follicle within a period of 4 months.
Dihydrotestosterone and Male Pattern Hair Loss
- ↑ "Hair Follicle". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved Nov 6, 2023.
- ↑ https://www.hairknowhow.com/know-your-hair-structure
Male pattern hair loss is primarily caused by genetics and dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. High levels of DHT can shrink the hair follicles and cause hair loss.[1] A DHT blocker such as dutasteride, finasteride can be used to prevent further hair loss, and minoxidil can be an effective treatment for hair loss. However, if you have testosterone suppressed, you likely don't need to block DHT.
- ↑ Cleveland Clinic. (12/20/2022). DHT (Dihydrotestosterone). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24555-dht-dihydrotestosterone
Pages in category "Hair Care"
The following 3 pages are in this category, out of 3 total.